
Golang在DevOps领域备受欢迎的原因之一,就是能够快速实现命令行工具。无论是多么复杂的源代码,最终都能够只被编译成一个简单的二进制可执行文件,这种极简的安装部署方式为开发带来极大的便利。
我们可以将Golang的编译产物直接移动到类似/usr/bin/或者/usr/local/bin/目录下,或者是将$GOPATH/bin添加到$PATH下。然后就像是使用基本shell命令一样去使用Golang的编译产物,这就是Golang命令行的基本原理。
框架与选型
实现Golang命令行工具的主流做法有两种:
- 基于标准包flag自定义实现
- 基于第三方框架实现
基于标准包flag自定义实现
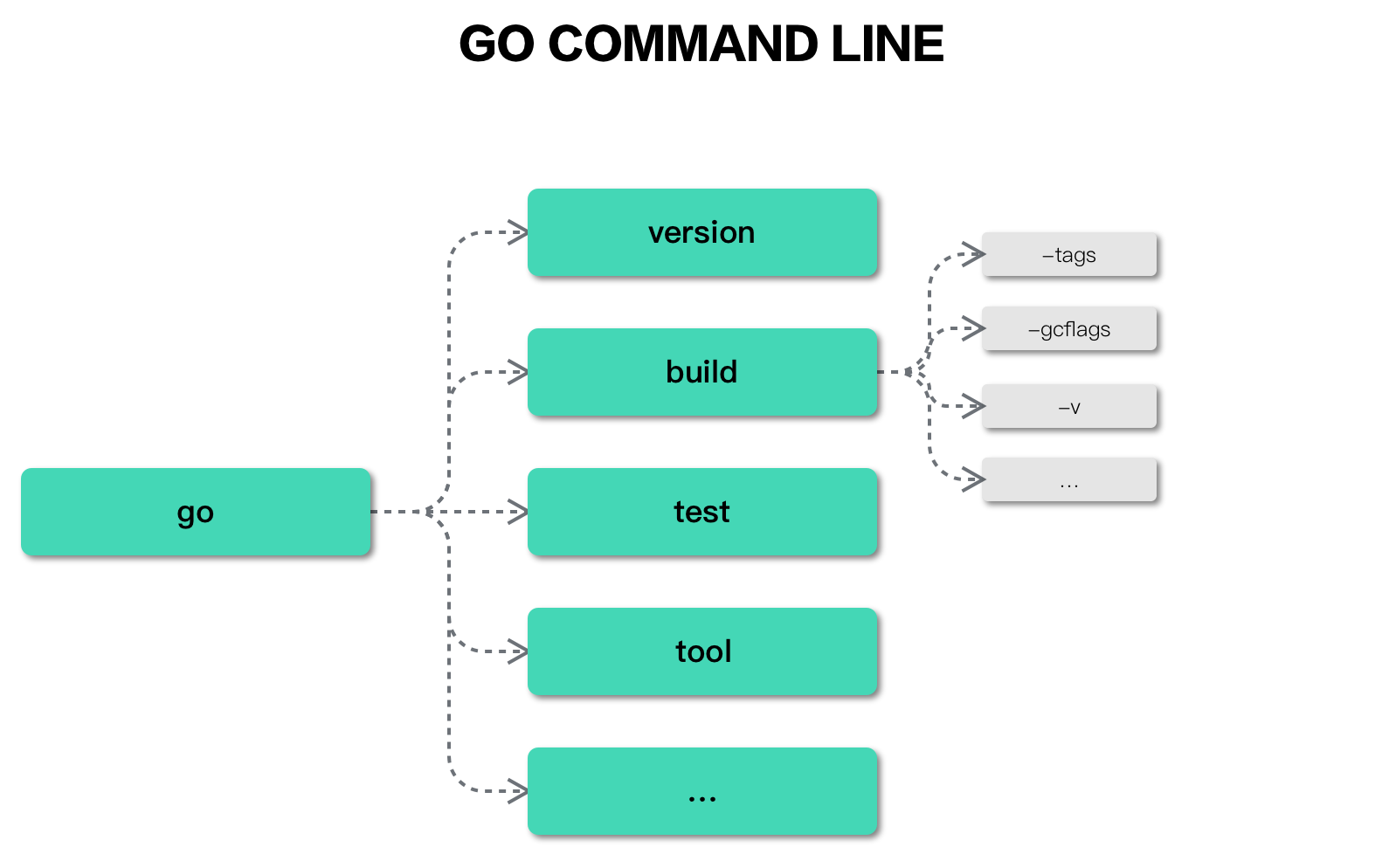
Golang自身实现官方工具go命令行(如下所示),就是基于flag包解析参数和自定义command类型来实现。
kevinwu@debian:~$ go
Go is a tool for managing Go source code.
Usage:
go <command> [arguments]
The commands are:
bug start a bug report
build compile packages and dependencies
clean remove object files and cached files
doc show documentation for package or symbol
env print Go environment information
fix update packages to use new APIs
fmt gofmt (reformat) package sources
generate generate Go files by processing source
get add dependencies to current module and install them
install compile and install packages and dependencies
list list packages or modules
mod module maintenance
run compile and run Go program
test test packages
tool run specified go tool
version print Go version
vet report likely mistakes in packages
Use "go help <command>" for more information about a command.
Additional help topics:
buildconstraint build constraints
buildmode build modes
c calling between Go and C
cache build and test caching
environment environment variables
filetype file types
go.mod the go.mod file
gopath GOPATH environment variable
gopath-get legacy GOPATH go get
goproxy module proxy protocol
importpath import path syntax
modules modules, module versions, and more
module-get module-aware go get
module-auth module authentication using go.sum
module-private module configuration for non-public modules
packages package lists and patterns
testflag testing flags
testfunc testing functions
Use "go help <topic>" for more information about that topic.
Command定义
我们来探究一下其源码实现,以当前最新的Go1.16为例:https://github.com/golang/go/blob/go1.16/src/cmd/go/internal/base/base.go
// A Command is an implementation of a go command
// like go build or go fix.
type Command struct {
// Run runs the command.
// The args are the arguments after the command name.
Run func(ctx context.Context, cmd *Command, args []string)
// UsageLine is the one-line usage message.
// The words between "go" and the first flag or argument in the line are taken to be the command name.
UsageLine string
// Short is the short description shown in the 'go help' output.
Short string
// Long is the long message shown in the 'go help <this-command>' output.
Long string
// Flag is a set of flags specific to this command.
Flag flag.FlagSet
// CustomFlags indicates that the command will do its own
// flag parsing.
CustomFlags bool
// Commands lists the available commands and help topics.
// The order here is the order in which they are printed by 'go help'.
// Note that subcommands are in general best avoided.
Commands []*Command
}
var Go = &Command{
UsageLine: "go",
Long: `Go is a tool for managing Go source code.`,
// Commands initialized in package main
}
Go源码中定义了Command结构体,并初始化了一个名为Go的实例,即go命令行。
其中需要重点注意的是:
- Flag字段是一组flags的集合
- Commands字段是一组sub commands的集合
- Run字段会定义command本身的运行逻辑
Command组织
举例来说:
kevinwu@debian:~/go/src/gogogo$ go build -gcflags "-N -l"
build是go命令行的一个sub command,而-gcflags "-N -l"是go build子命令行的一个flag,go build本身的逻辑就是源码中Run字段定义的部分。
go命令行定义了一系列的sub command:https://github.com/golang/go/blob/go1.16/src/cmd/go/main.go
func init() {
base.Go.Commands = []*base.Command{
bug.CmdBug,
work.CmdBuild,
clean.CmdClean,
doc.CmdDoc,
envcmd.CmdEnv,
fix.CmdFix,
fmtcmd.CmdFmt,
generate.CmdGenerate,
modget.CmdGet,
work.CmdInstall,
list.CmdList,
modcmd.CmdMod,
run.CmdRun,
test.CmdTest,
tool.CmdTool,
version.CmdVersion,
vet.CmdVet,
help.HelpBuildConstraint,
help.HelpBuildmode,
help.HelpC,
help.HelpCache,
help.HelpEnvironment,
help.HelpFileType,
modload.HelpGoMod,
help.HelpGopath,
get.HelpGopathGet,
modfetch.HelpGoproxy,
help.HelpImportPath,
modload.HelpModules,
modget.HelpModuleGet,
modfetch.HelpModuleAuth,
help.HelpPackages,
modfetch.HelpPrivate,
test.HelpTestflag,
test.HelpTestfunc,
modget.HelpVCS,
}
}
从源码中我们可以看出一些熟悉的身影,例如go build、go test、go tool等等。每个子命令都会包含一个Run方法,定义具体的运行逻辑,以go build为例:https://github.com/golang/go/blob/go1.16/src/cmd/go/internal/work/build.go
func init() {
// break init cycle
CmdBuild.Run = runBuild // 给Run字段赋值,是一个执行方法
CmdInstall.Run = runInstall
CmdBuild.Flag.BoolVar(&cfg.BuildI, "i", false, "")
CmdBuild.Flag.StringVar(&cfg.BuildO, "o", "", "output file or directory")
CmdInstall.Flag.BoolVar(&cfg.BuildI, "i", false, "")
AddBuildFlags(CmdBuild, DefaultBuildFlags)
AddBuildFlags(CmdInstall, DefaultBuildFlags)
}
// 执行方法的具体运行逻辑
func runBuild(ctx context.Context, cmd *base.Command, args []string) {
BuildInit()
var b Builder
b.Init()
pkgs := load.PackagesAndErrors(ctx, args)
load.CheckPackageErrors(pkgs)
explicitO := len(cfg.BuildO) > 0
if len(pkgs) == 1 && pkgs[0].Name == "main" && cfg.BuildO == "" {
cfg.BuildO = pkgs[0].DefaultExecName()
cfg.BuildO += cfg.ExeSuffix
}
// sanity check some often mis-used options
switch cfg.BuildContext.Compiler {
case "gccgo":
if load.BuildGcflags.Present() {
fmt.Println("go build: when using gccgo toolchain, please pass compiler flags using -gccgoflags, not -gcflags")
}
if load.BuildLdflags.Present() {
fmt.Println("go build: when using gccgo toolchain, please pass linker flags using -gccgoflags, not -ldflags")
}
case "gc":
if load.BuildGccgoflags.Present() {
fmt.Println("go build: when using gc toolchain, please pass compile flags using -gcflags, and linker flags using -ldflags")
}
}
depMode := ModeBuild
if cfg.BuildI {
depMode = ModeInstall
fmt.Fprint(os.Stderr, "go build: -i flag is deprecated\n")
}
pkgs = omitTestOnly(pkgsFilter(pkgs))
// Special case -o /dev/null by not writing at all.
if cfg.BuildO == os.DevNull {
cfg.BuildO = ""
}
if cfg.BuildO != "" {
// If the -o name exists and is a directory or
// ends with a slash or backslash, then
// write all main packages to that directory.
// Otherwise require only a single package be built.
if fi, err := os.Stat(cfg.BuildO); (err == nil && fi.IsDir()) ||
strings.HasSuffix(cfg.BuildO, "/") ||
strings.HasSuffix(cfg.BuildO, string(os.PathSeparator)) {
if !explicitO {
base.Fatalf("go build: build output %q already exists and is a directory", cfg.BuildO)
}
a := &Action{Mode: "go build"}
for _, p := range pkgs {
if p.Name != "main" {
continue
}
p.Target = filepath.Join(cfg.BuildO, p.DefaultExecName())
p.Target += cfg.ExeSuffix
p.Stale = true
p.StaleReason = "build -o flag in use"
a.Deps = append(a.Deps, b.AutoAction(ModeInstall, depMode, p))
}
if len(a.Deps) == 0 {
base.Fatalf("go build: no main packages to build")
}
b.Do(ctx, a)
return
}
if len(pkgs) > 1 {
base.Fatalf("go build: cannot write multiple packages to non-directory %s", cfg.BuildO)
} else if len(pkgs) == 0 {
base.Fatalf("no packages to build")
}
p := pkgs[0]
p.Target = cfg.BuildO
p.Stale = true // must build - not up to date
p.StaleReason = "build -o flag in use"
a := b.AutoAction(ModeInstall, depMode, p)
b.Do(ctx, a)
return
}
a := &Action{Mode: "go build"}
for _, p := range pkgs {
a.Deps = append(a.Deps, b.AutoAction(ModeBuild, depMode, p))
}
if cfg.BuildBuildmode == "shared" {
a = b.buildmodeShared(ModeBuild, depMode, args, pkgs, a)
}
b.Do(ctx, a)
}
小结
总结一下,整个Command的设计结构是比较清晰的,通过sub commands和flags来区分不同的功能,进入不同的Run方法。
基于第三方框架实现
基于第三方框架实现命令行的原理与上述相同,也是基于flag包解析参数,同时自定义Command结构体。不过第三方框架通常已经定义好成熟稳定且功能丰富的Command,开发者只需要简单复用其框架即可快速开发出高效的命令行工具。
目前Go开源项目中有两个较为热门的框架:
这两个项目的功能差不多,不过相比之下cobra的名气更大一些,基于cobra命令行的知名项目有:Kubernetes、Hugo、Github CLI等。
优势
基于第三方框架的核心优势在于开箱即用,无需开发者重复发明轮子。以cobra为例,框架能够提供如下的核心功能:
- 子命令支持
- 参数alias支持
- 默认生成帮助界面
- 命令行自动补全
小结
对于Go官方工具链来说,不使用第三方框架是为了不依赖第三方框架,使得Go语言自身形成闭环,这是一个重要的设计原则。但对于大部分开发者来说,如果没有特殊情况,一致推荐基于cobra或cli来定制命令行工具,不仅风格统一,而且开发效率非常高。
实战
接下来的篇幅中,笔者将会基于cobra从0开始完成一个cli-demo,体验开发一个命令行工具的全流程。
创建RootCommand
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/spf13/cobra"
"os"
)
var RootCommand = &cobra.Command{
Use: "cli",
Short: "cli is demo for cobra",
Run: func(cmd *cobra.Command, args []string) {
},
}
func main() {
if err := RootCommand.Execute(); err != nil {
fmt.Fprintln(os.Stderr, err)
os.Exit(1)
}
}
创建SubCommand
var BuildSubCommand = &cobra.Command{
Use: "build",
Run: func(cmd *cobra.Command, args []string) {
},
}
var TestSubCommand = &cobra.Command{
Use: "test",
Run: func(cmd *cobra.Command, args []string) {
},
}
func init() {
RootCommand.AddCommand(BuildSubCommand)
RootCommand.AddCommand(TestSubCommand)
}
新增Flags
RootCommand.Flags().BoolP("update", "u", false, "")
整体预览
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/spf13/cobra"
"os"
)
var RootCommand = &cobra.Command{
Use: "cli",
Short: "cli is demo for cobra",
Run: func(cmd *cobra.Command, args []string) {
},
}
var BuildSubCommand = &cobra.Command{
Use: "build",
Run: func(cmd *cobra.Command, args []string) {
},
}
var TestSubCommand = &cobra.Command{
Use: "test",
Run: func(cmd *cobra.Command, args []string) {
},
}
func init() {
RootCommand.AddCommand(BuildSubCommand)
RootCommand.AddCommand(TestSubCommand)
RootCommand.Flags().BoolP("update", "u", false, "")
}
func main() {
if err := RootCommand.Execute(); err != nil {
fmt.Fprintln(os.Stderr, err)
os.Exit(1)
}
}
编译运行
- 编译
$ go build
- cli-demo
$ ./cli-demo --help
cli is demo for cobra
Usage:
cli [flags]
cli [command]
Available Commands:
build
help Help about any command
test
Flags:
-h, --help help for cli
-u, --update
Use "cli [command] --help" for more information about a command.
- 子命令
$ ./cli-demo build --help
Usage:
cli build [flags]
Flags:
-h, --help help for build
小结
总的来说,基于cobra的命令行开发流畅并且功能强大,自动生成的帮助说明更是风格统一,充分展现出了一款精心设计命令行的优美。
总结
本文简要介绍了Golang命令行工具开发的原理和框架,并以一个极简的cli-demo为大家展示基于cobra框架的开发流程,强烈推荐有同样需求的场景使用!